Table of contents
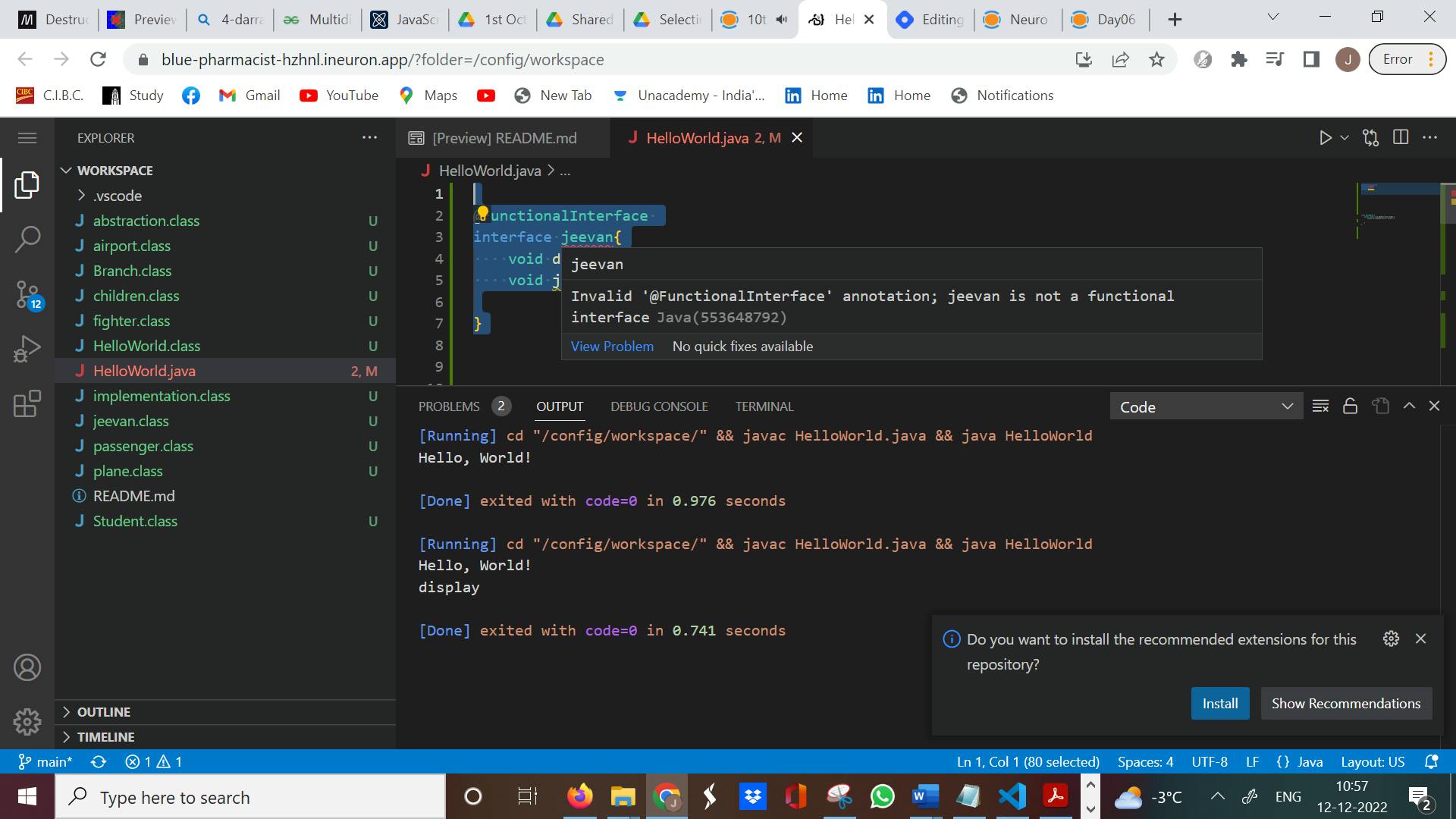
Functional Interface
- If an interface has only one abstract method in it then such an interface is called as a functional interface
- We can give the implementation using a lambda expression, anonymous inner class
- We can also implement it using other interface
- Using interface
interface jeevan{
void disp();
}
class implementation implements jeevan{
public void disp(){
System.out.println("display");
}
}
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
implementation object = new implementation();
object.disp();
}
}
- Functional Interface we use '@ functional interface' else we will get an error
Anonymous Inner Class
- Types of Anonymous Inner Class
a. Anonymous Inner class that extends a class b. Anonymous Inner class that implements an interface c. Anonymous Inner class that defines inside method/constructor argument
a. Anonymous inner class for implementing an interface example:
@FunctionalInterface
interface jeevan{
void disp();
}
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
jeevan object = new jeevan(){
public void disp(){
System.out.println("hi");
}
};
object.disp();
}
}
b. Anonymous Inner class that extends a class for method overriding-- use this when we only want to use the overridden method only once
example:
class jeevan{
public void disp(){
System.out.println("jeevan");
}
}
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
jeevan object = new jeevan(){
public void disp(){
System.out.println("hi");
}
};
object.disp();
}
}
Another method of doing this
interface computer{
void disp();
}
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
/*computer object =new computer(){
public void disp(){
System.out.println("hi");
}
};
object.disp(); */ // why to write this we can use short cut called as lambda function
computer object = () ->
{
System.out.println("short code");
};
object.disp();
}
}
Note : We can use lambda function only with functional interface
